
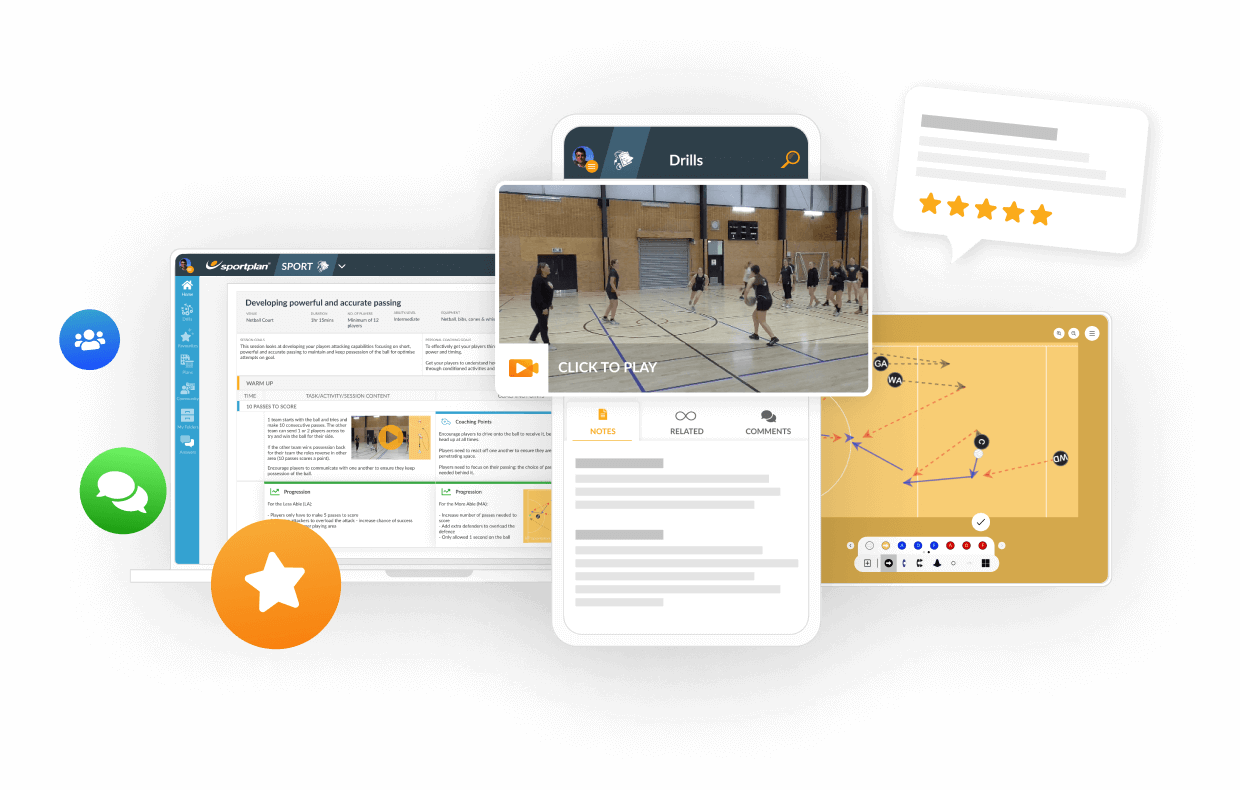
This drill helps players to practise securing space by bodying up to the defender to protect the space in which they want to receive the ball. Working in 3s, feeder, attacker, defender. Initially, the defender is static. Attacker retrieves a dropped ball from F Passes the ball back to the F Race back to the D front on and "seals" them in place. Use upright body only, no arms! Opens up body / step open, hips (widest part of body) to keep the seal, whilst presenting for ball. Repeat 4-6 times and swap Progression: D can now move within a small space (still not going for ball, just adjusting position) A now has to sight as early as possible to seal If A has hands out feeling for D as they return, let the D grab them and prevent the turn! Progression A has a bib tucked down back of shorts to encourage her to make the seal and turn close to body (and not step off as they turn) If there is a gap, then the D can steal in (but they shouldn't steal it if there is no gap!) Can also profress to bib front and back! Progression (advanced) Take onto court relevant to position This time A should react to what the D does: - D stays still = can the A front cut to get ball down court? - D steps forward to prevent the front cut = can A seal and present? - D steps forward and covers the angle (to prevent the seal) = can A roll around for the lifted long ball? Q: is the D actually stopping upi or just making you uncomfortable? Force the D to make a decision and react off that!
Quick reactions and open visions are key in this practuse How close can the A get to the D ? You may need to practise deceleration You may need to encourage an actual physical touch to encourage to get close enough depending on age and ability How quickly can they find the defender and secure their space? Feet under body, body upright (not creating contact) Which shoulder to turn? Hips across infront of D when you complete turn - don't let them slip by! Arms down - not feeling for defender, use for momentum to sprint off once sealed. Force the D to make a decision and use this as a tool in your toolbox!
This practice has no coaching points
This practice has no progressions
in more ways than one
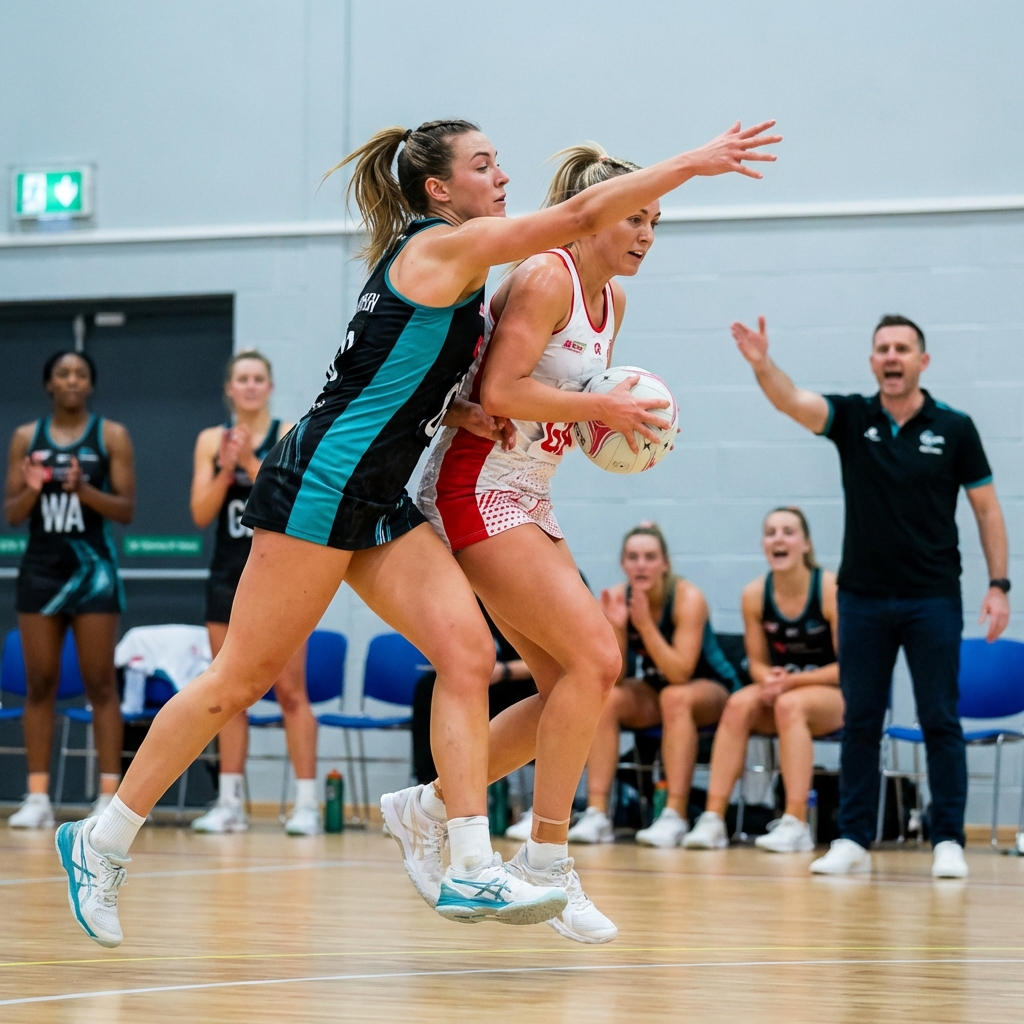



No more 50/50 toss-ups. When simultaneous infringements occur, possession now goes to the team that last had the ball. Here's what it means for your coaching.
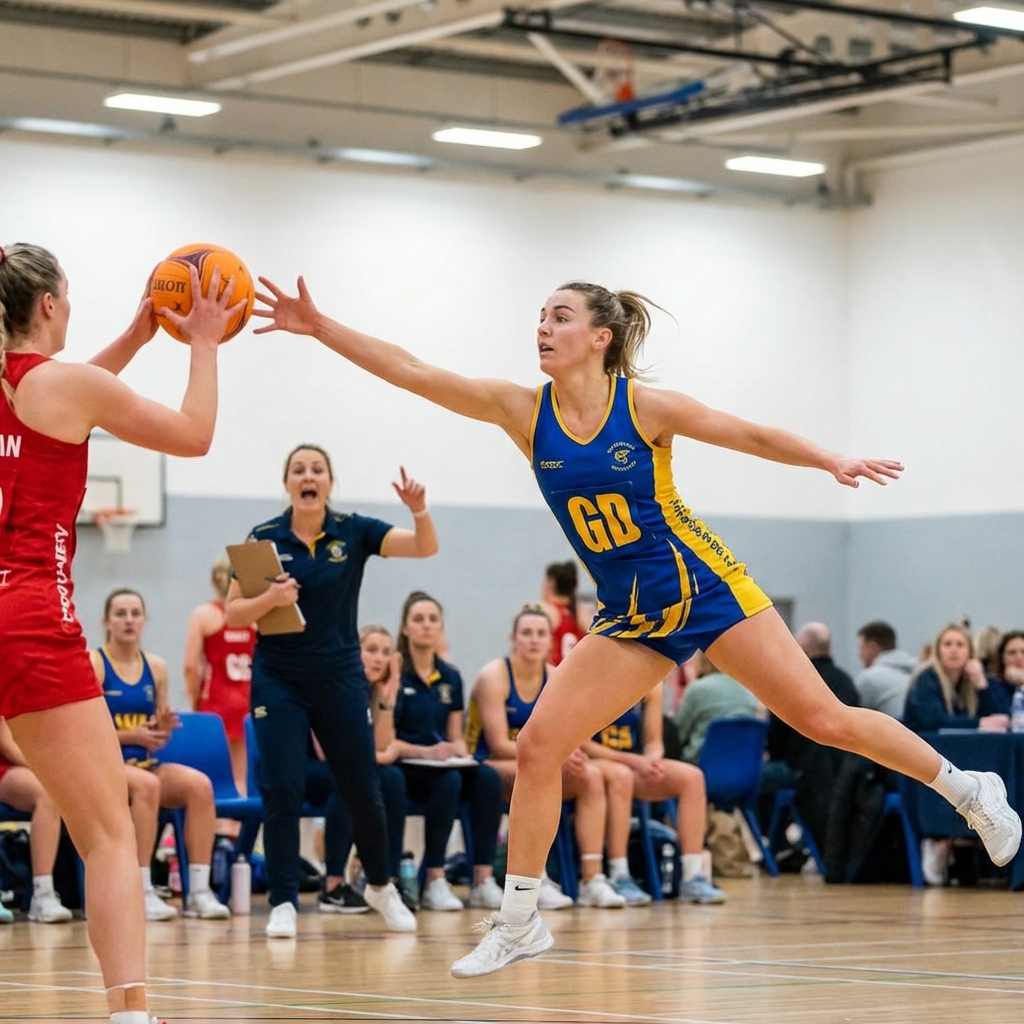

Train your defenders to win clean turnovers, not just disrupt. The difference between good defenders and great ones is taking the ball, not just touching it.
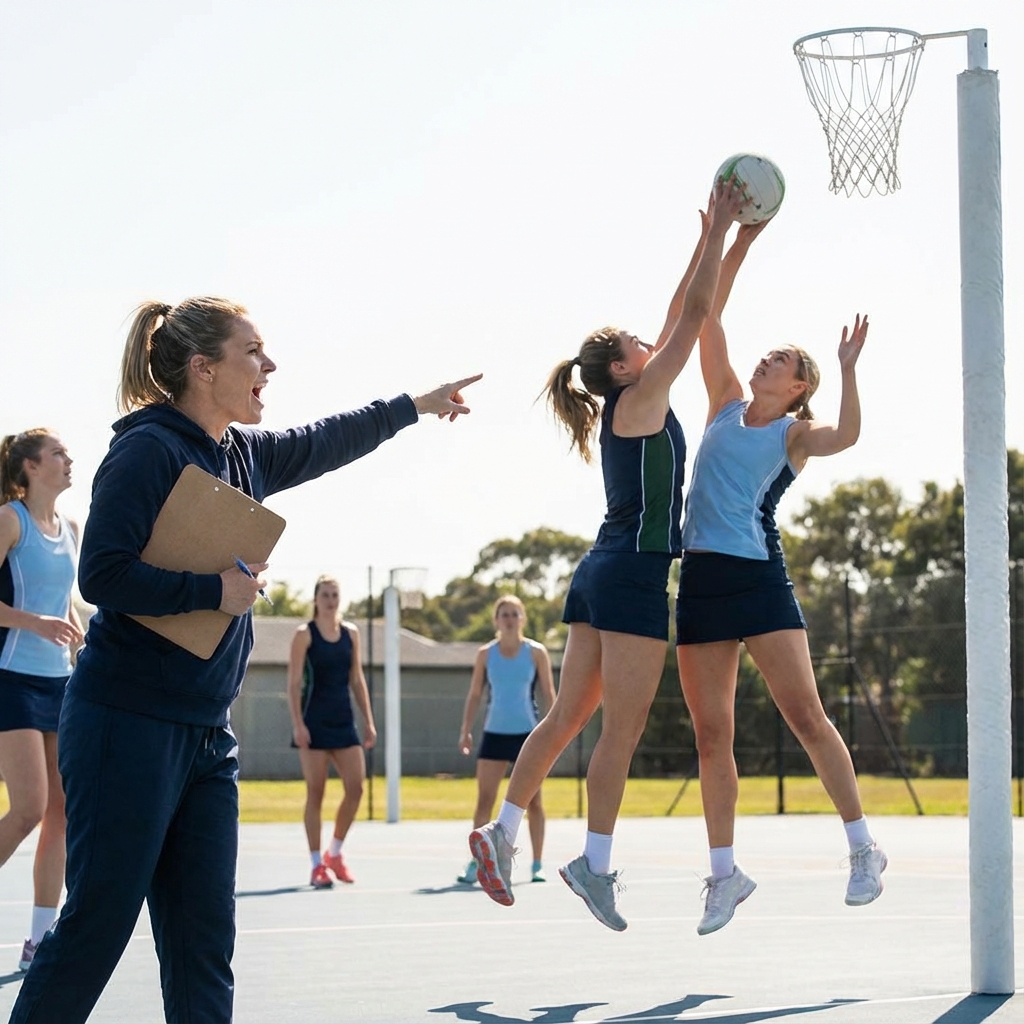

Netball is experiencing unprecedented growth, with record viewership, evolving rules, and professional leagues expanding worldwide. Here's what 2026 brings for our sport.