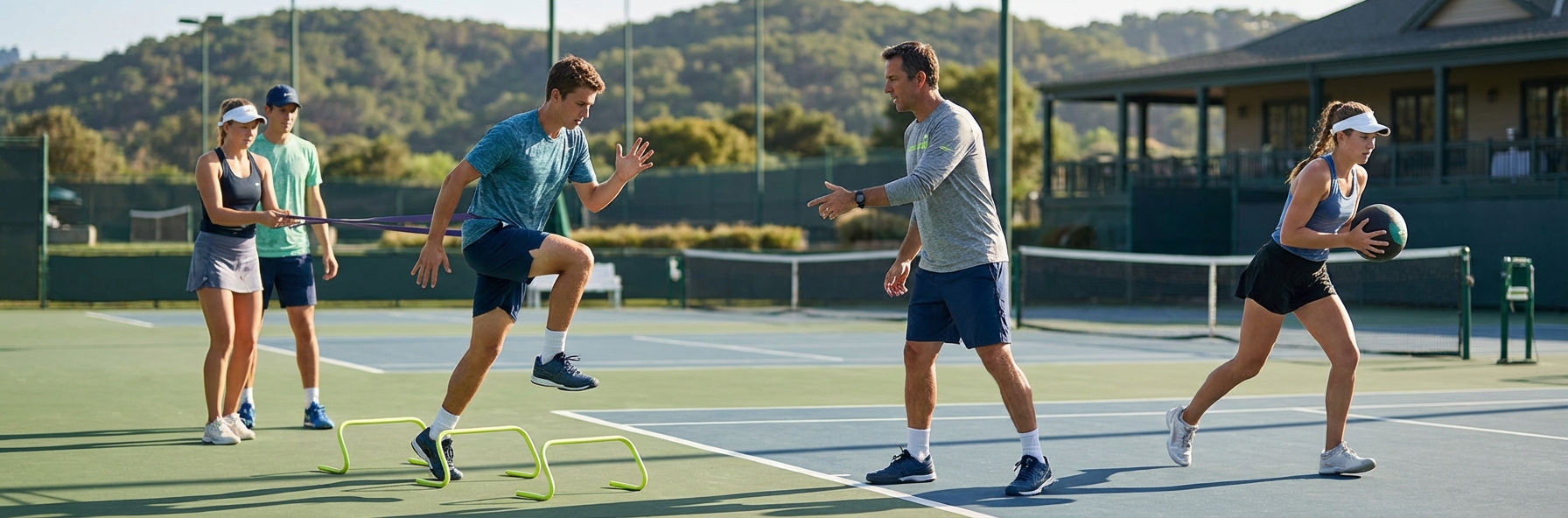
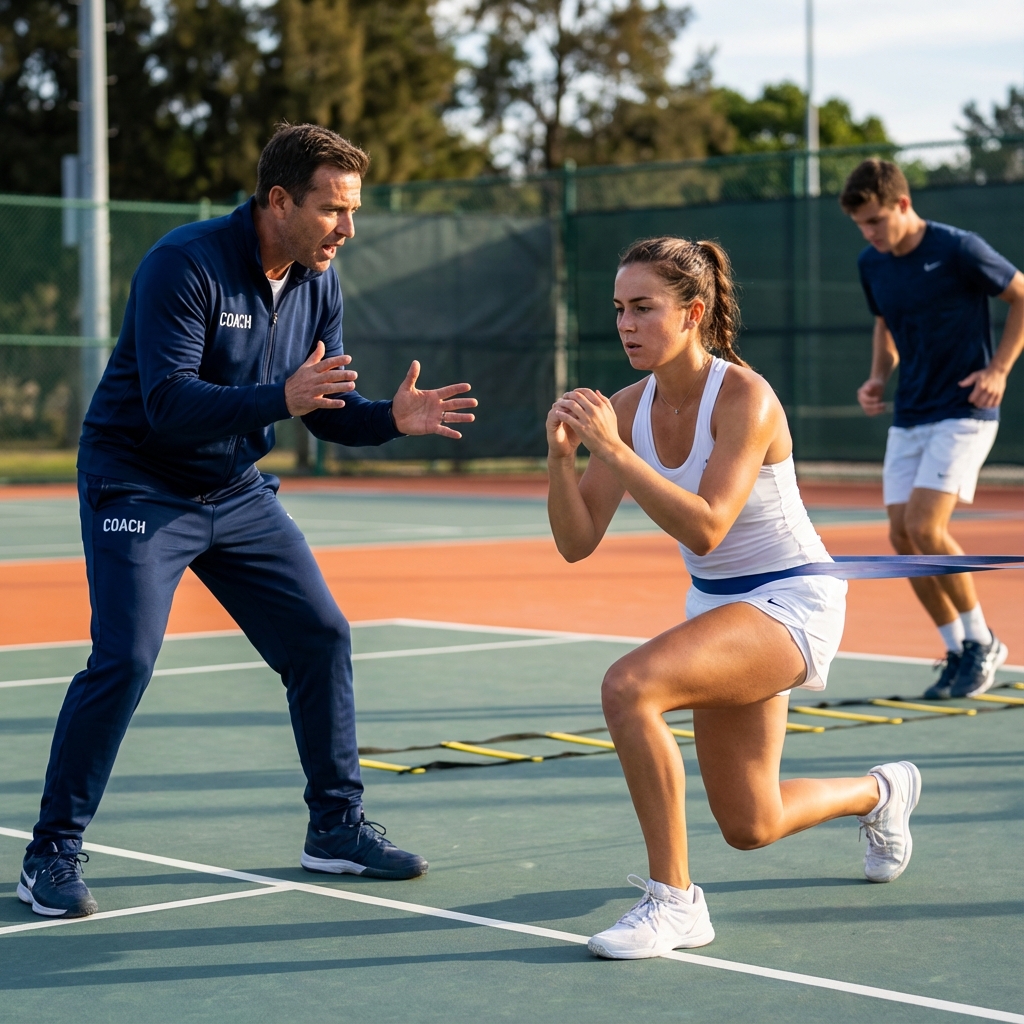
Tennis is one of the most physically demanding sports. Matches can last five hours. Players cover 3-5 kilometres per match in explosive sprints. They rotate their bodies hundreds of times, generating forces that stress muscles, tendons, and joints. The best technique in the world fails without the physical foundation to support it.
Modern tennis preparation addresses all components of athletic performance - not just "getting fit."
Physical Demands of Tennis
Understanding what tennis requires:
Intermittent power: Tennis is repeated bursts of high-intensity activity with brief recovery. Average points last 6-10 seconds with 15-20 seconds between points.
Multi-directional movement: Forward, backward, lateral, diagonal - often in the same point. Change of direction is as important as straight-line speed.
Unilateral loading: Dominant arm and leg do more work, creating imbalances that need addressing.
Duration: Matches can last hours. Maintaining quality in the fifth set requires aerobic fitness most players underestimate.
Strength Training
Strength provides the foundation:
Lower body: Squats, lunges, and deadlifts build the leg strength for explosive movement and stable bases.
Core: Rotational power comes from the core. Medicine ball throws, cable rotations, and plank variations are essential.
Upper body: Balanced development prevents shoulder injuries. Push and pull movements in equal measure.
Unilateral work: Single-leg and single-arm exercises address the asymmetries tennis creates.
Power Development
Strength without speed is incomplete:
Plyometrics: Jump training develops explosive power - box jumps, bounds, depth jumps.
Medicine ball throws: Sport-specific power development. Rotational throws mimic the power generation in strokes.
Speed training: Short sprints with full recovery. Quality over quantity.
Agility work: Ladder drills, cone patterns, reactive movement training.
Endurance Training
The aerobic base enables everything else:
Aerobic capacity: Long, steady-state training builds the cardiovascular foundation. Essential for match-long performance and recovery between points.
Interval training: More tennis-specific than steady state. Work/rest ratios that mimic match demands.
On-court conditioning: Drills that combine technical work with physical demand. Efficient use of training time.
Heat adaptation: For players competing in hot conditions, progressive heat exposure builds tolerance.
Flexibility and Mobility
Range of motion affects performance and injury risk:
Dynamic stretching: Pre-training movement preparation. Leg swings, arm circles, trunk rotations.
Static stretching: Post-training and maintenance work. Hold positions for 30+ seconds.
Targeted areas: Hip flexors, shoulders, thoracic spine, and hamstrings typically need most attention.
Foam rolling: Self-myofascial release maintains tissue quality.
Recovery
Training creates adaptation only if recovery is adequate:
Sleep: The most important recovery tool. 8-10 hours for developing athletes.
Nutrition: Adequate protein, carbohydrates to fuel training, hydration. Match nutrition is specific science.
Active recovery: Light movement promotes blood flow without adding training stress.
Recovery modalities: Massage, cold water immersion, compression - all have roles in tournament settings.
Injury Prevention
Training should reduce injury risk:
Shoulder health: Rotator cuff strengthening and scapular stability work protect against overuse injuries.
Ankle stability: Balance work and ankle strengthening prevent sprains.
Gradual progression: Training load increases gradually. Large spikes in volume or intensity cause injuries.
Movement quality: Proper technique in training exercises prevents compensation patterns.
Periodisation
Training must be planned across the year:
Off-season: Higher volumes, building foundations. Less tennis, more physical training.
Pre-competition: Transition to sport-specific work. Intensity increases, volume decreases.
In-season: Maintenance focus. Enough to sustain fitness without compromising match performance.
Tournament blocks: Minimal physical training during competitions. Focus on recovery.
Key Coaching Points
- Tennis demands a unique combination of power, endurance, agility, and flexibility
- Strength training provides the foundation for all other physical qualities
- Recovery is training - sleep, nutrition, and rest days are not optional
- Injury prevention must be built into every training programme
- Training periodisation matches physical preparation to the competition calendar