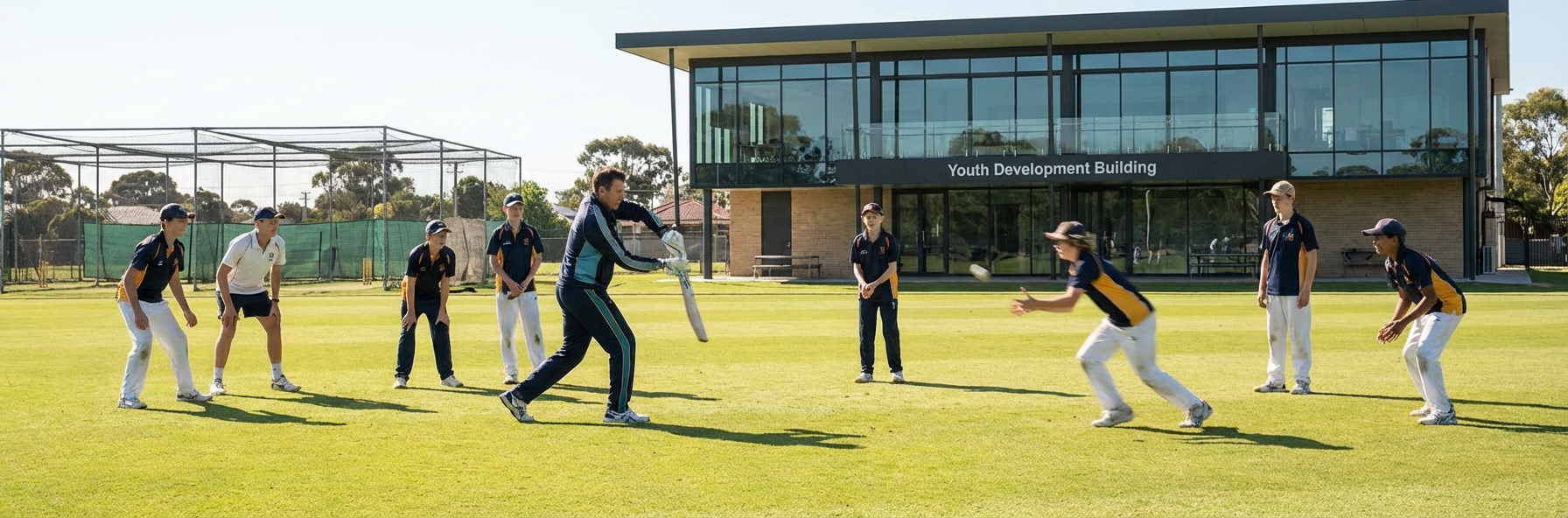
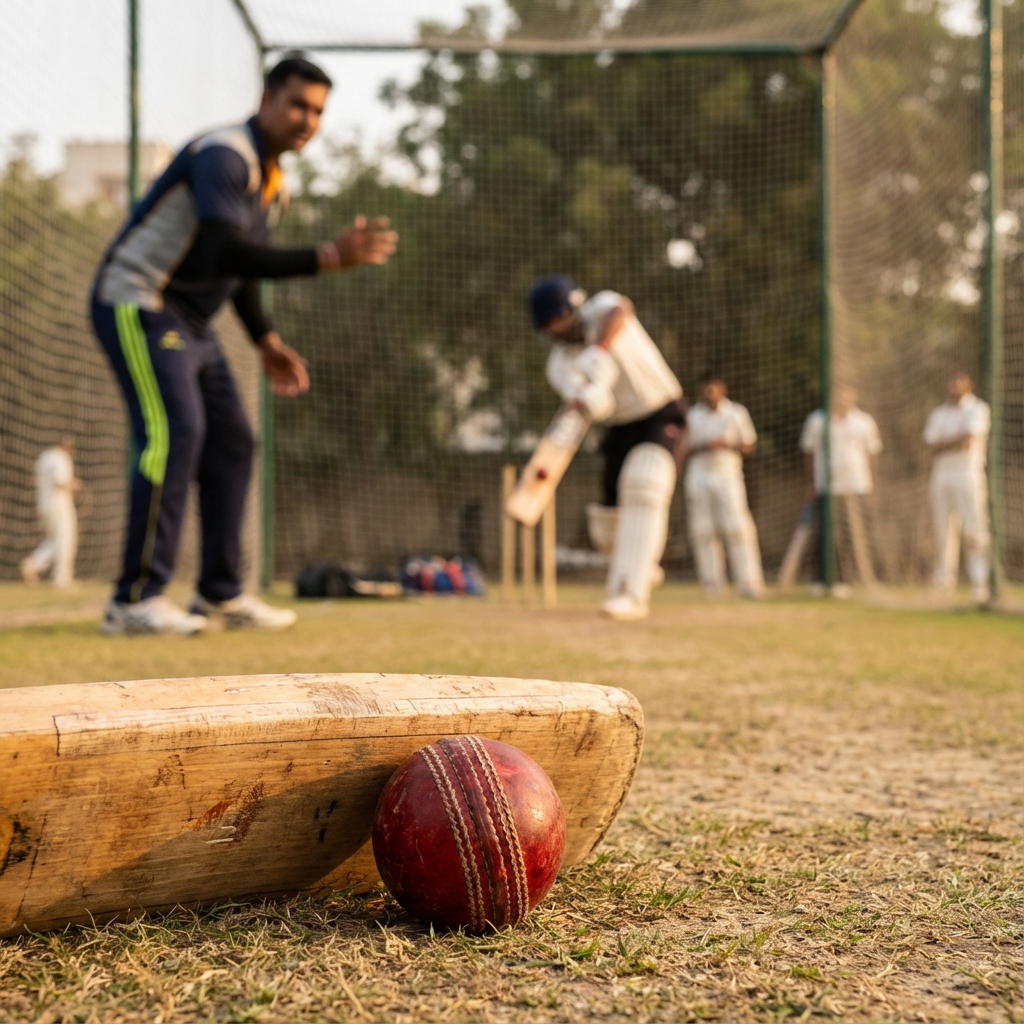
The ICC Training and Education platform has achieved over 30,000 course completions across 173 countries. This global reach emphasises the importance of structured youth development that produces well-rounded cricketers capable of contributing with bat, ball, and in the field.
Age-Appropriate Development
Matching training to developmental stage:
Under 10: Fun, basic motor skills, hand-eye coordination through games.
10-12: Technical foundations in batting, bowling, and fielding.
12-14: Skill refinement, introduction to tactics and game awareness.
14-16: Specialisation begins while maintaining all-round skills.
Avoiding Early Specialisation
Multi-skill exposure: Young players should experience all disciplines.
Injury prevention: Varied activities reduce overuse injuries.
Late development: Some elite players develop skills in their late teens.
Mental engagement: Variety maintains enthusiasm and love for the game.
Fun-Based Learning
Modified games: Kwik Cricket and adapted formats keep players engaged.
Competition balance: Enough competition to develop, not so much it creates pressure.
Success experiences: Design activities where all players can succeed.
Social development: Team activities build friendships and commitment.
Coach Development
ICC pathways: Level 1, 2, and now Level 3 coaching certifications.
Age-specific training: Understanding how children learn differently from adults.
Safety awareness: Appropriate training loads and injury prevention.
Positive environments: Creating cultures that retain young players.
Key Coaching Points
- Develop all skills before allowing specialisation
- Fun and engagement drive long-term participation
- Match training intensity to developmental stage
- Modified games provide maximum participation
- Coach education is essential for quality youth development