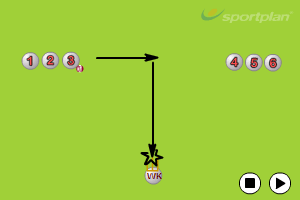
Fielding standards in professional cricket have risen dramatically. Run-saving in the outfield, direct hit run-outs, and athletic boundary saves are now expected rather than exceptional. Developing these skills requires dedicated training and athletic conditioning.
Ground Fielding Fundamentals
Clean collection under pressure:
Long barrier technique: Getting the body behind the ball for guaranteed stops.
Two-handed pickup: Secure collection when time allows.
One-handed flick: Quick release for run-out opportunities.
Sliding stops: Athletically covering ground to cut off boundaries.
Throwing Accuracy
Crow hop technique: Building momentum for powerful, accurate throws.
Target focus: Throwing at the stumps, not to the keeper.
Flat trajectory: Direct throws reach the target faster than lobs.
Weak arm development: Ability to throw accurately with either arm.
Athletic Movement
Anticipation: Reading the shot and moving early.
Explosive starts: Quick acceleration to cut off shots.
Diving technique: Safe, effective diving for catches and stops.
Recovery speed: Getting back in position quickly after fielding.
Team Fielding Coordination
Backing up: Ensuring overthrows don't cost extra runs.
Communication: Clear calls for catches and throwing targets.
Rotation: Fresh fielders in key positions at crucial moments.
Pressure maintenance: Keeping dot ball intensity in the field.
Key Coaching Points
- Fielding is a skill that requires dedicated practice time
- Athletic conditioning supports fielding performance
- Direct hit accuracy improves with targeted practice
- Team coordination multiplies individual fielding efforts
- High fielding standards create pressure on batting teams