
Two Defensive lines
When and where does defensive play begin? When? As soon as the opponent has the ball Where? In any area of the pitch: ⢠In the opponentâs final third: try to stop the opponent from launching an attack ⢠In the midfield: try to slow down the opponentâs move ⢠In a teamâs own final third: protect the goal Using: â the selected formation â the basic position of the unit on the pitch â the playersâ individual characteristics â players who do more than their roles demand â respect for the teamâs balance Defending = a job for the whole team Regardless of the formation used, the type of play or the basic position of the team unit, the coach has to ensure that all of his players understand that one system is used and that each player knows: â what he has to do â where he has to do it â when he has to do it â how he has to do it Putting such a system in place revolves around two questions: â Where should the teamâs attempts to regain possession start? â How will these attempts be organised? The system will also take three key things into account, namely: â The ball carrier â Time â Space
This practice has no coaching points
This practice has no progressions
in more ways than one
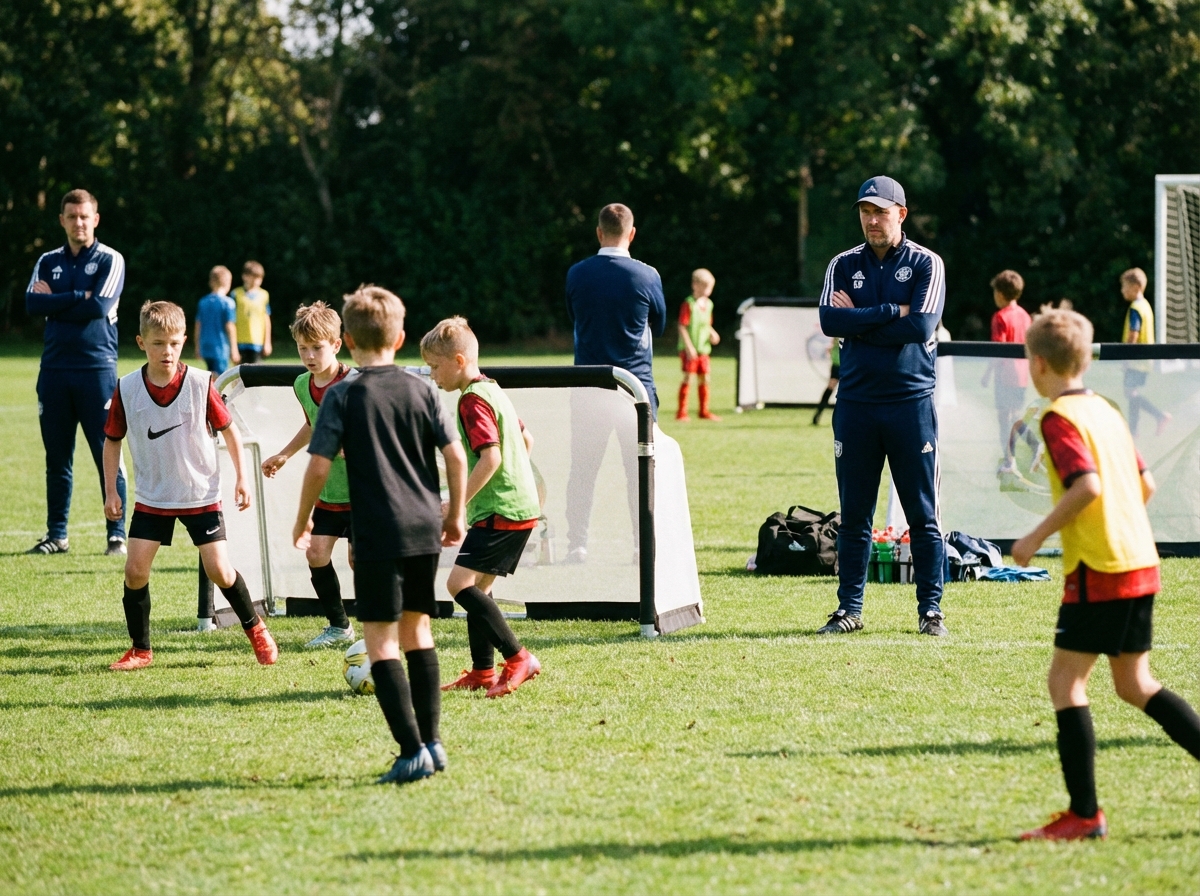




The coaching methodology revolution sweeping grassroots football - and how to implement it at your club this season.
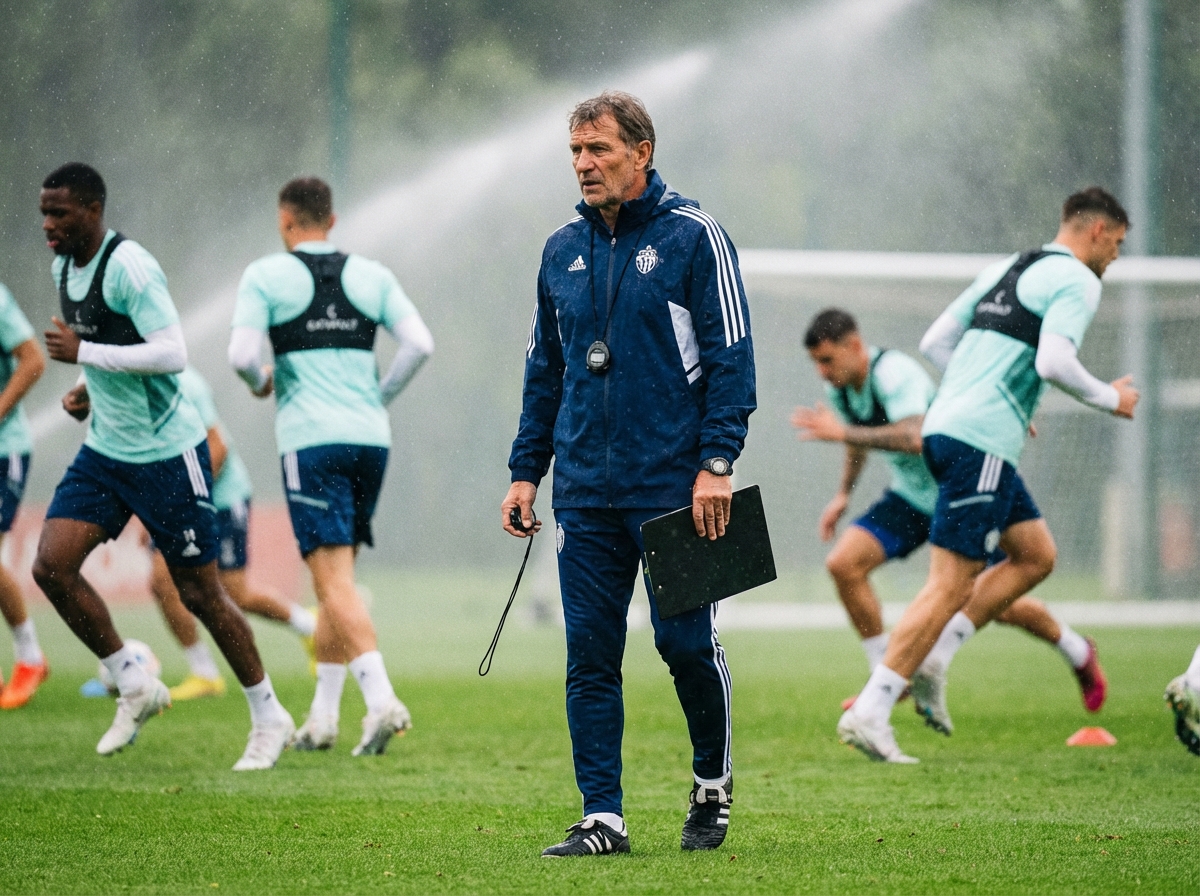

Why the best coaches in 2026 are measuring intensity, not just running drills - and how you can do it without expensive technology.
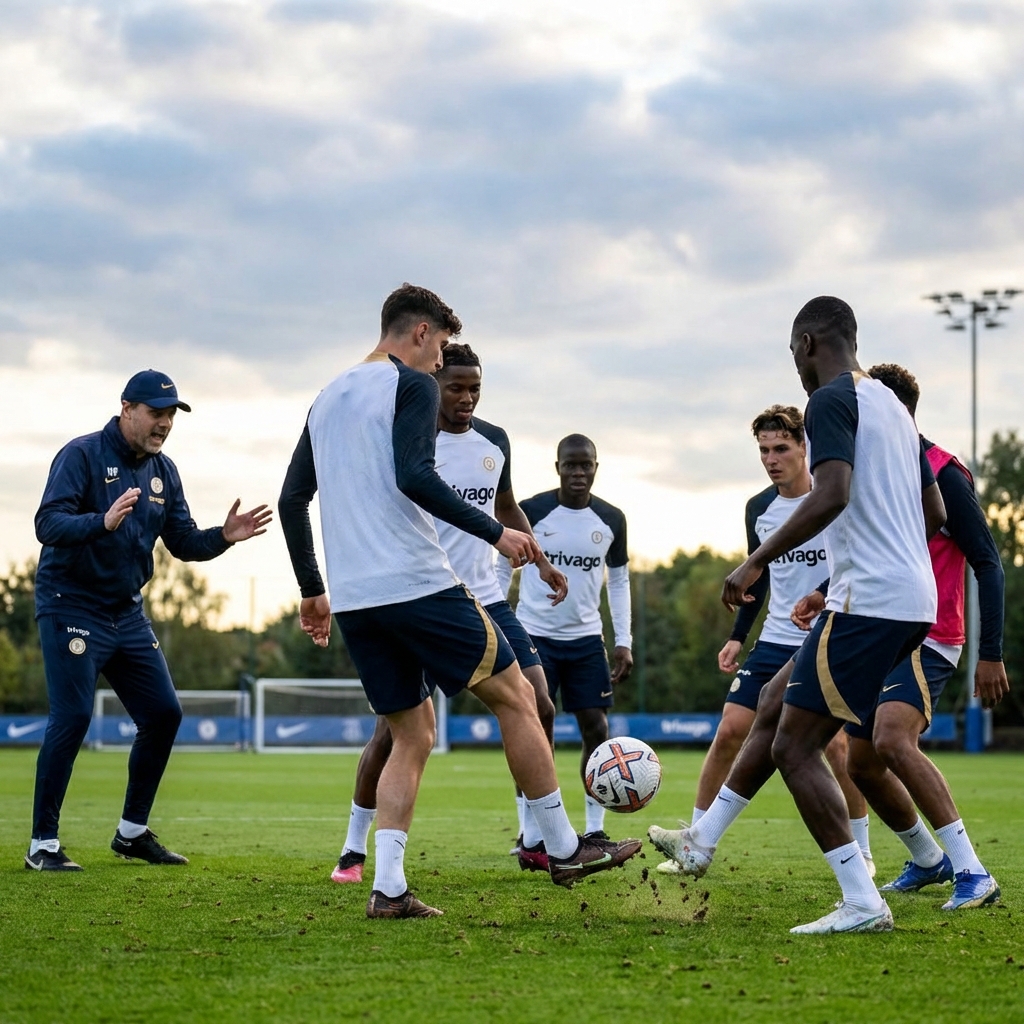

Why Barcelona's favourite training exercise should be in every coach's toolkit - and how to run rondos that actually transfer to matches.